Biodiversity
Home > Biodiversity
Coastal Forests of Eastern Africa
VCSL’s project contributes to protection of high biodiversity value habitats
The Village Land Forest Reserves, which cover the Noto Plateau and buffer the Chitoa Plateau, are part of the Coastal Forests of Eastern Africa. This ecosystem is recognized as a global biodiversity hotspot, home to numerous rare and endemic species. The project’s biodiversity survey has confirmed that the ecosystem supports the Rondo Dwarf Galago (a primate) and African Savannah Elephants, both classified as endangered species on the IUCN Red List. Additionally, the survey identified three endangered and four vulnerable plant species, with two of the endangered plant species being found exclusively in the Noto Plateau forests within the project area.
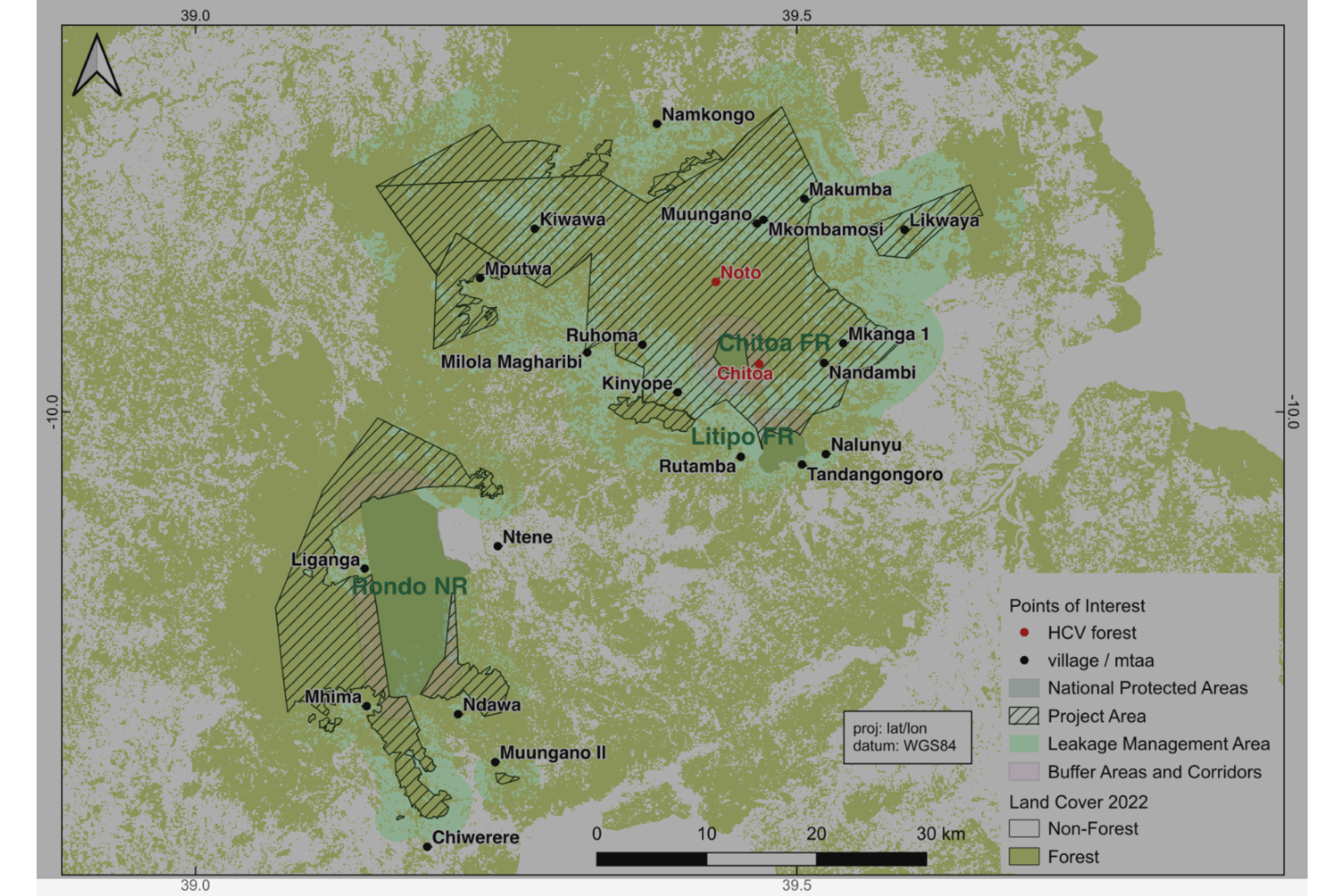
The project’s zonal map for Mtama and Lindi Municipality showing Noto and Chitoa Plateaus
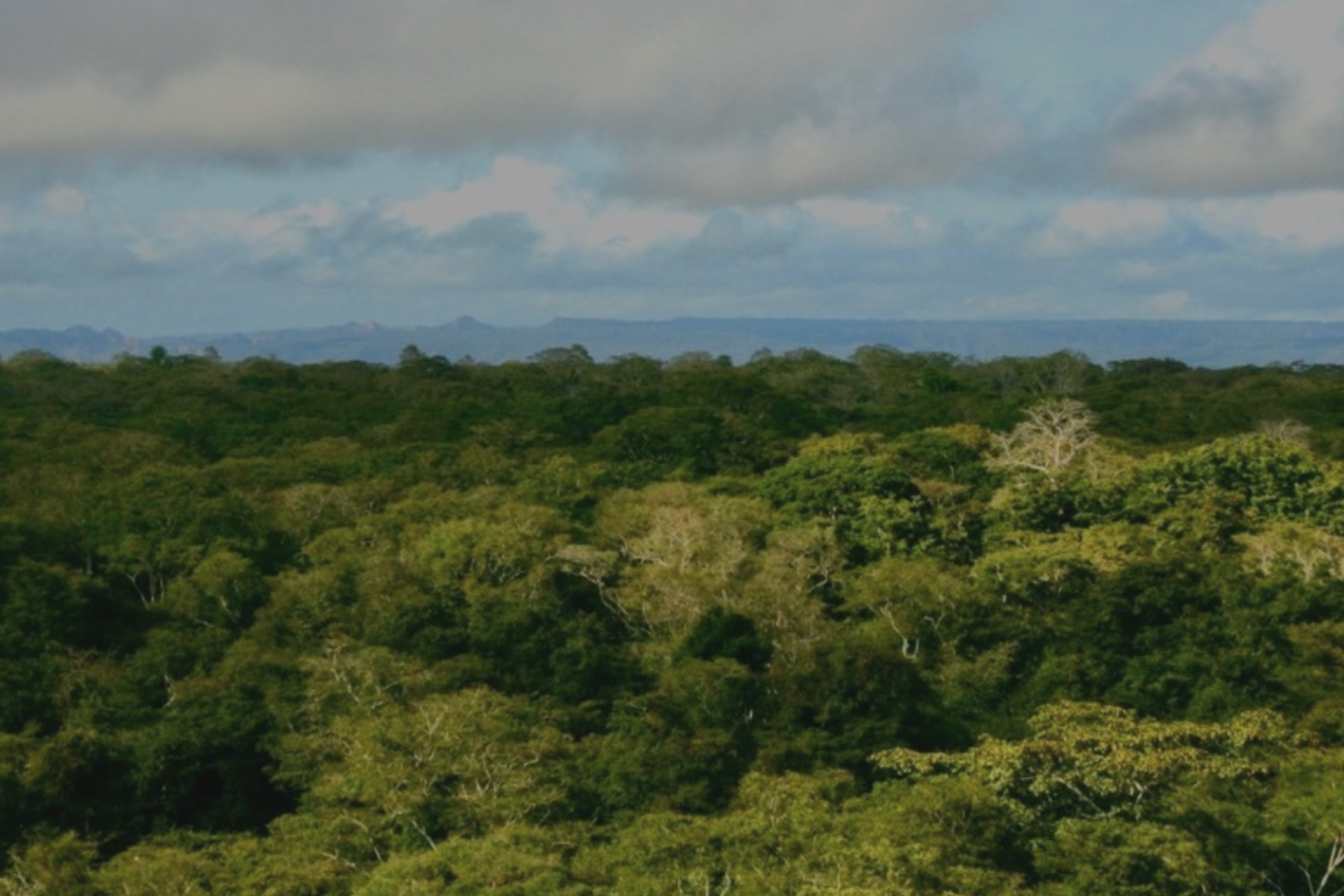

Noto Plateau Coastal Forest in Muungano Village
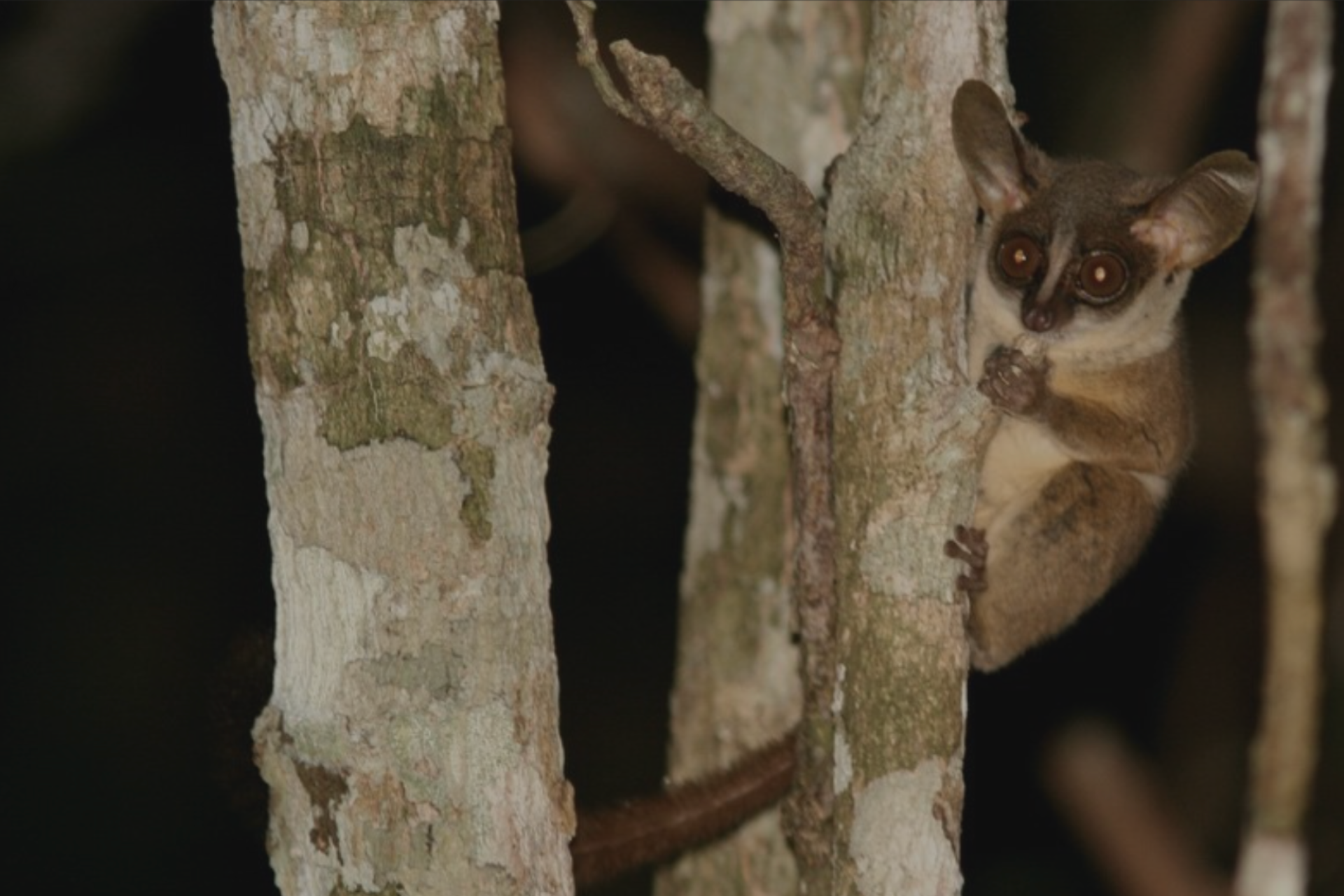

Rondo Dwarf Galago from Noto Plateau (Paragalago rondoensis)
Eastern Arc Mountain Forest
The Ilole Forest, which includes the Malolo A, Kisanga, and Msimba Village Land Forest Reserves, is part of the Eastern Arc Mountain Forest ecosystem. This area is recognized as a global biodiversity hotspot, home to many rare and endemic species.
Ilole Forest is inhabited by at least three IUCN-endangered species: Abbot’s duiker, African Savannah Elephant, and Keetia davidii (a plant), as well as at least three IUCN-vulnerable species: Mountain Dwarf Galago (a primate), Uluguru Banana Frog, and Uluguru Forest Snake.
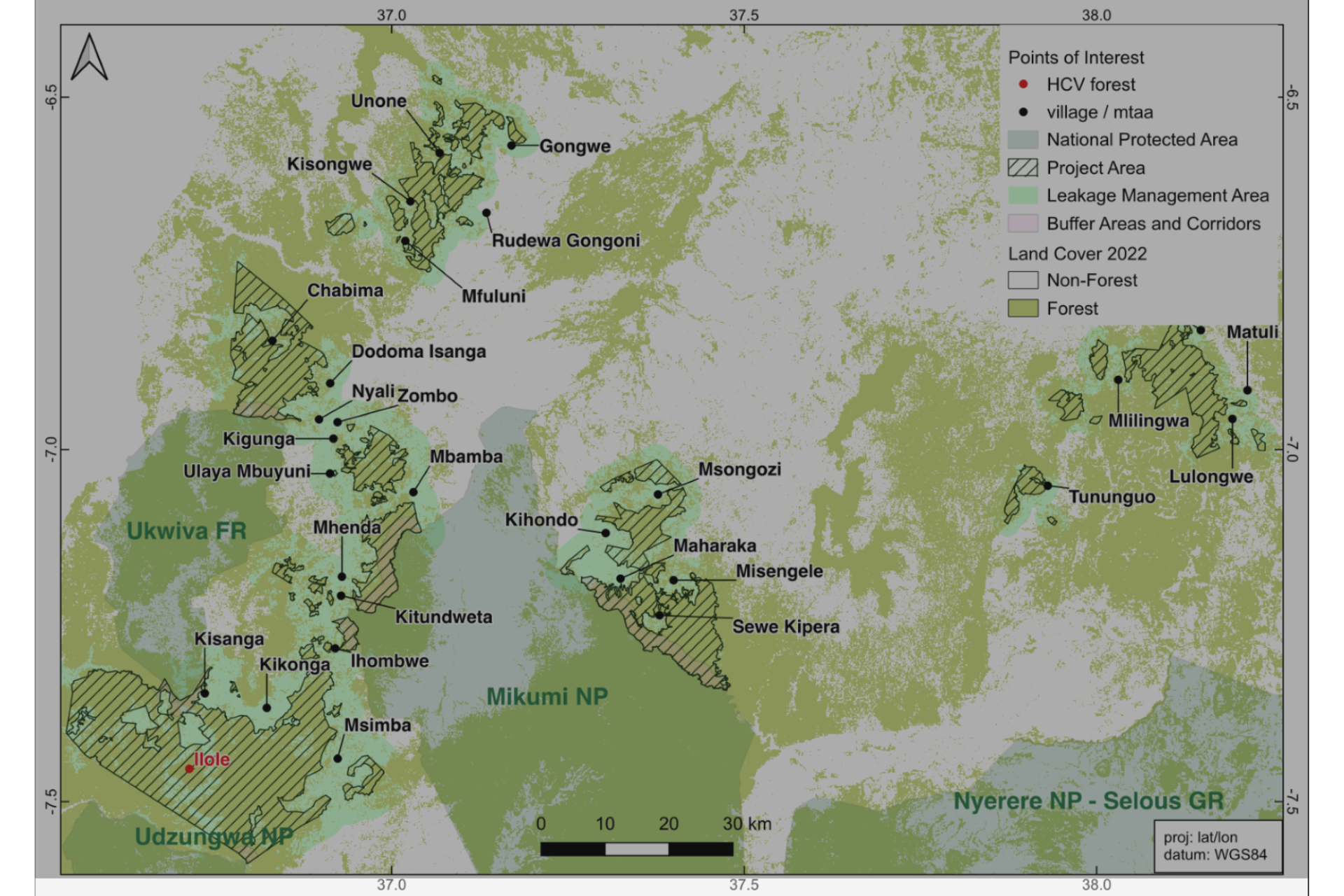
Project Zone in Morogoro, Mvomero, and Kilosa Districts, showing Ilole Mountain Forests and buffer areas to National Protected Area
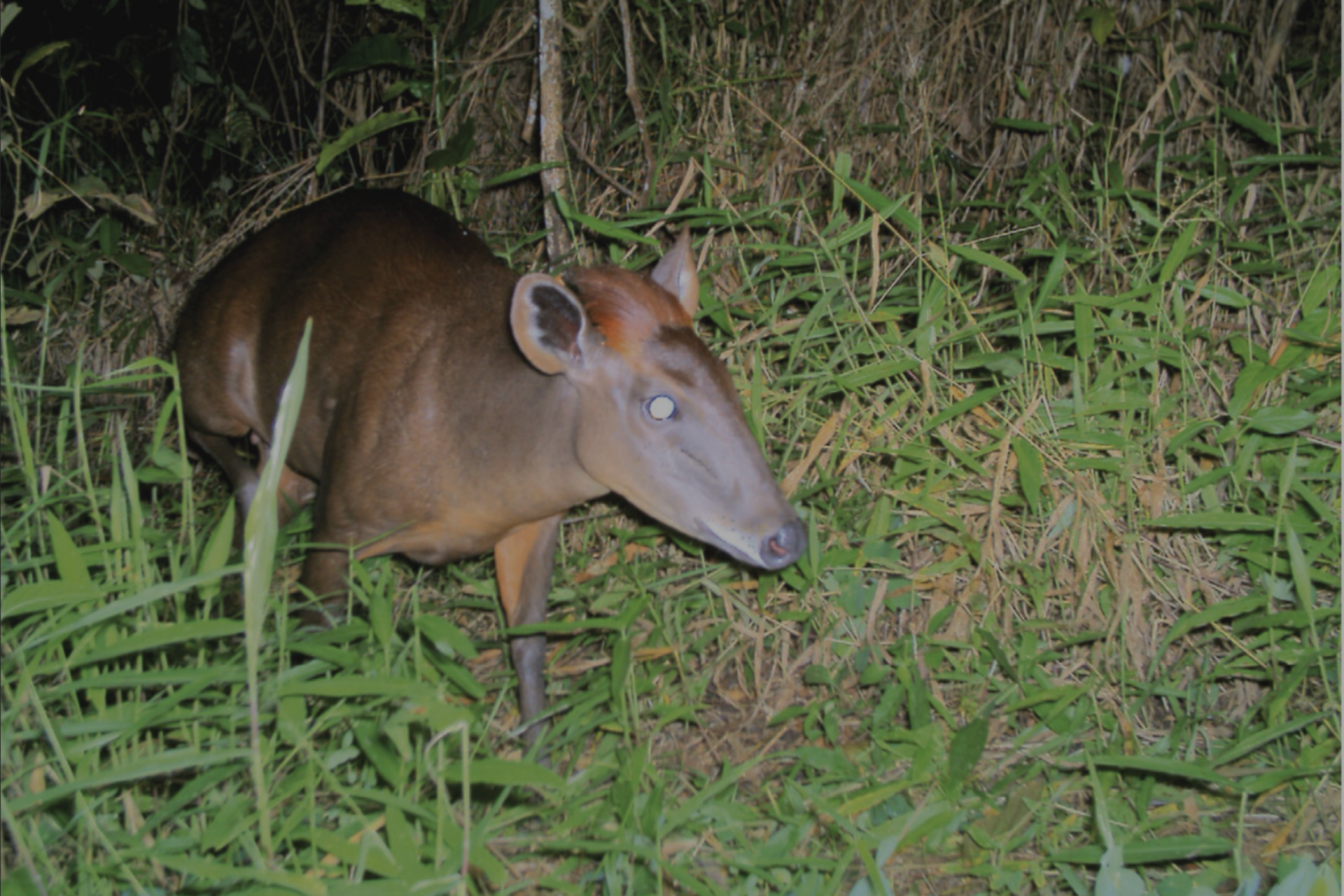

Abbott’s Duiker (Cephalophus spadix) (Bowkett et al., 2014)
Wildlife Corridors and Buffer Areas to Protected Areas
The project area provides significant buffer zones for national protected areas and serves as important wildlife corridors.
- Five Village Land Forest Reserves namely; Sewe Kipera, Maharaka, Mhenda, Kitundweta, and Ihombwe, serve as buffers to Mikumi National Park.
- Three Village Land Forest Reserves namely; Kisanga, Malolo A, and Nyali, provide significant buffering for Ukwiva Forest Reserve.
- Seven Village Land Forest Reserves namely; Mtua, Chimbendenga, Mbondo, Majonanga, Matekwe, Majengo, and Mkumbaru, offer important buffer areas for Msanjesi Game Reserve.
- Four Village Land Forest Reserves namely; Mbondo, Majonanga, Nakolonji, and Nahimba, create a wildlife corridor of natural woodland linking Msanjesi Game Reserve to wilderness areas in Liwale District, which connects to Nyerere National Park, the Selous Game Reserve to the south, and the Niassa Game Reserve in northern Mozambique.
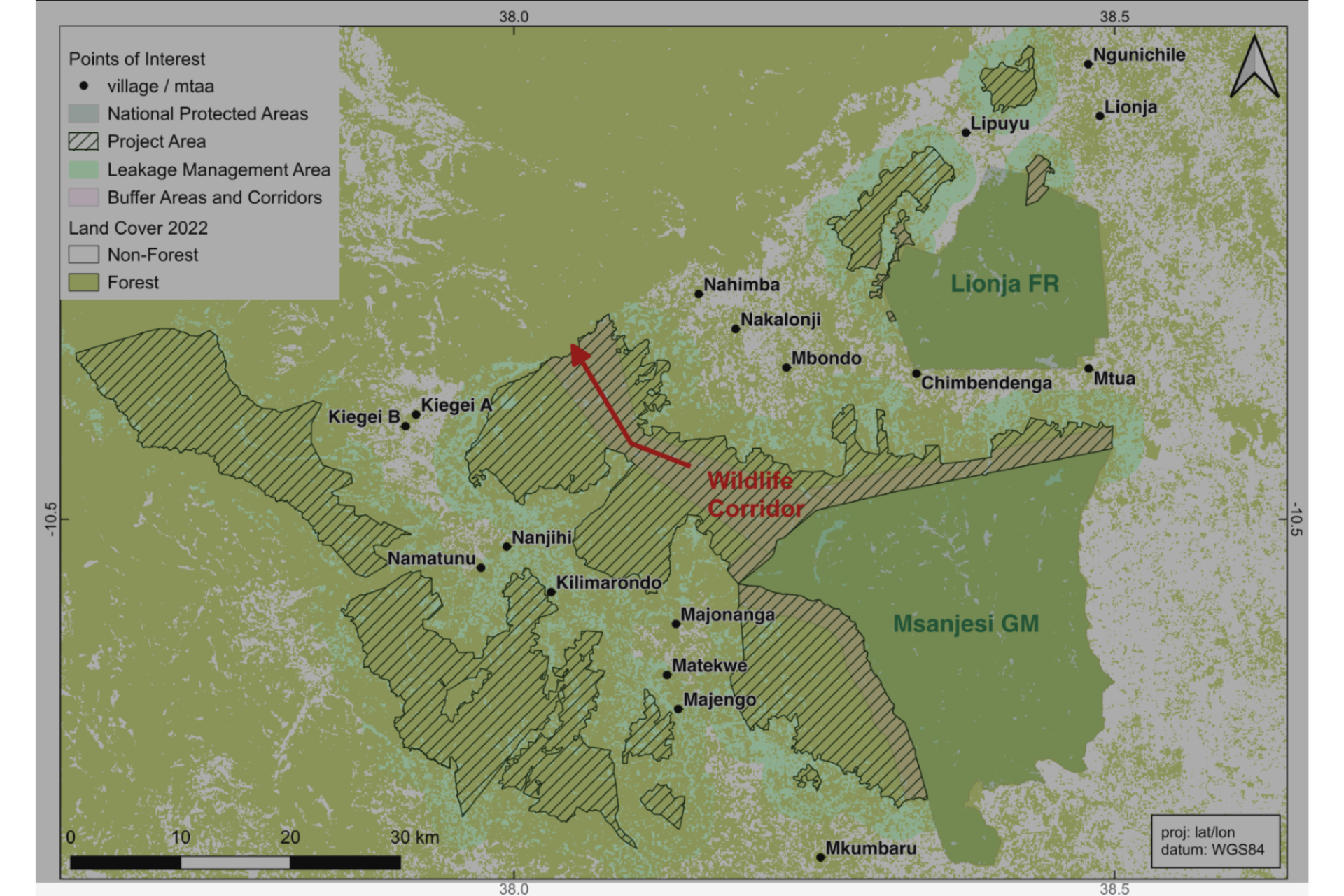
Project Zone in Nachingwea and Nanyumbu Districts indicating buffer areas and wildlife corridor to Msanjesi Game Reserves.
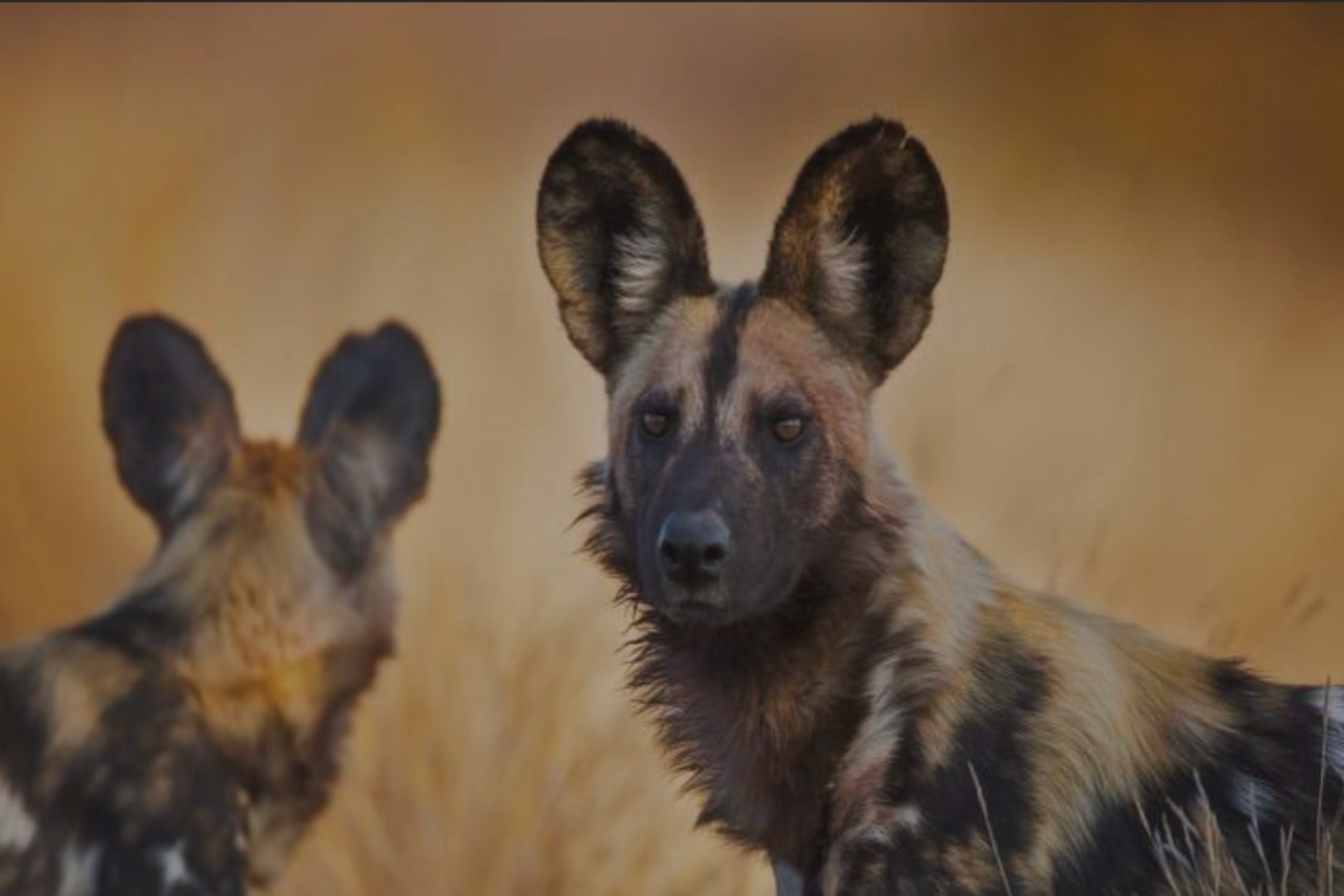

African Wild Dog (Lycaon pictus)
Miombo
Most Village Land Forest Reserves consist of large blocks of Miombo forests, characterized by diverse tree species such as Brachystegia, Julbernardia, and Isoberlinia. These forests are rich in biodiversity, supporting a wide range of flora and fauna. They provide habitats for iconic wildlife, including elephants, antelopes, and primates, as well as numerous endemic and threatened plant and animal species. Their ecological diversity plays a vital role in maintaining ecosystem services and supporting local livelihoods.
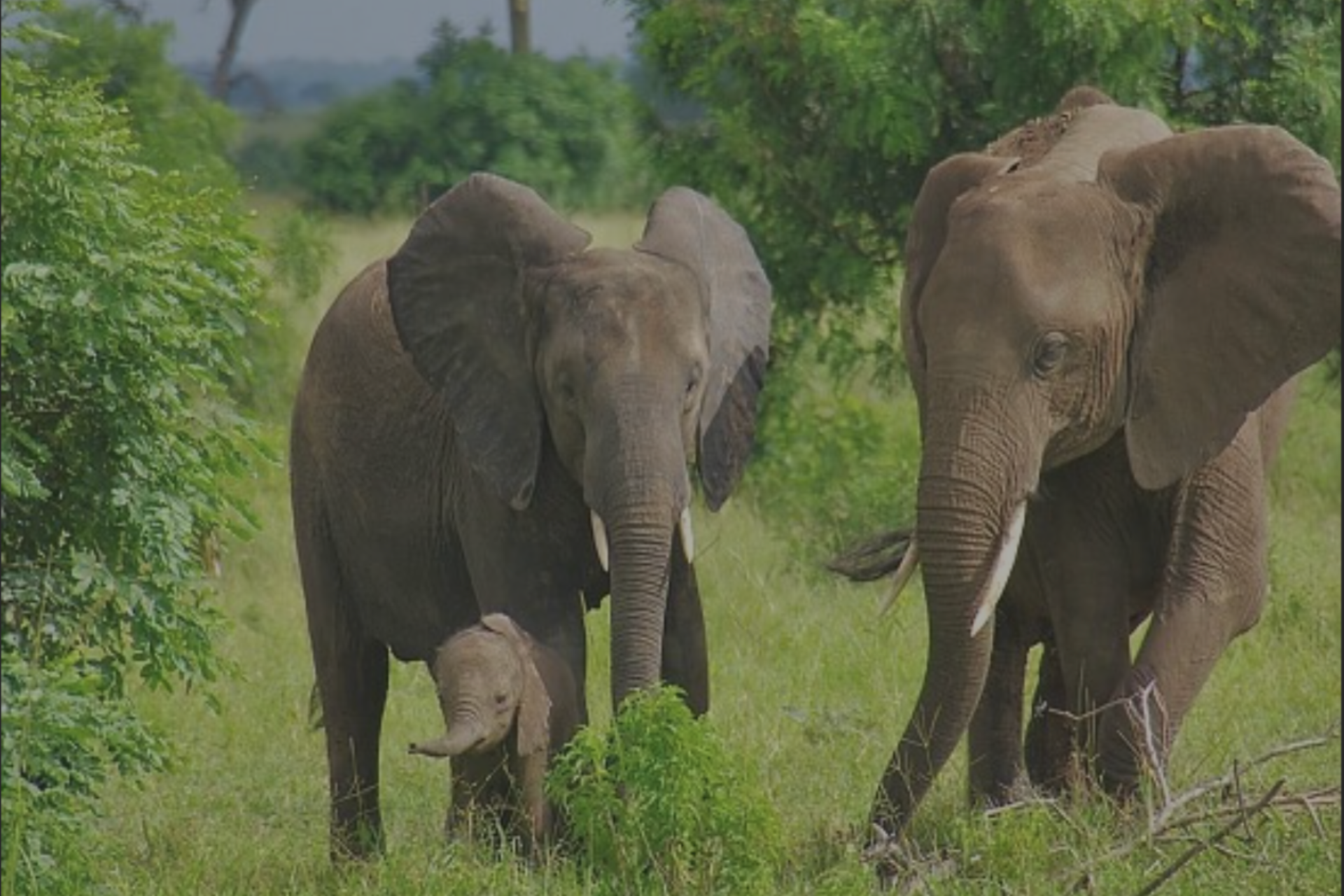

African Savanah Elephant (Loxodonta africana)
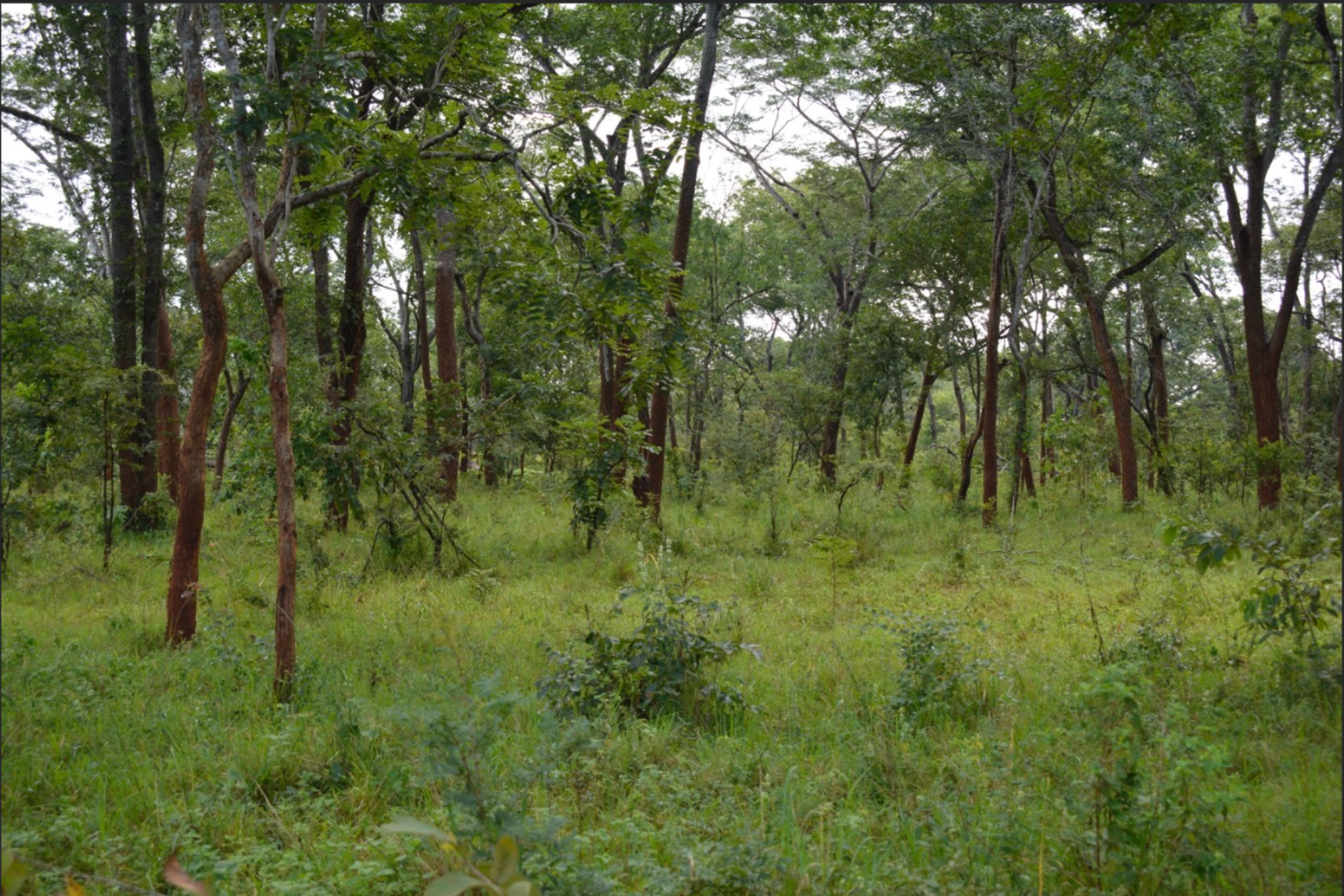

Miombo forest in Nachingwea

